水泥混凝土路面由于具有寿命长、施工简便以及养护工作量小等优点,在中国公路通车里程中占有很大比例。但是,水泥混凝土路面在使用一段时间后,表面砂浆层容易被磨光,导致表面构造快速下降,严重影响行车安全[1-3]。此时,路面结构完好,仅需恢复表面构造。可以采用硬刻槽重新对水泥混凝土路面饰纹,但工作量大、效率低,且粉尘污染严重,还可能造成结构损坏;同时,表面构造存在再次被磨光的可能。因此,近年来一些工程采取沥青薄层罩面改善其表面特性[4],但由于结构、材料和使用环境等影响,水泥混凝土路面沥青薄层罩面结构易产生罩面层滑移、拥包等破坏,影响了路面的使用。
水泥路面沥青薄层罩面结构层间稳定性吸引了很多学者关注。楚留声等[5]通过低周反复荷载试验研究水泥混凝土的黏结性能。Nian等[6]分析了剪切应力比、加载频率、温度和冻融循环对层间剪切疲劳的影响,建立了层间剪切疲劳寿命预测模型。曹明明等[7]通过试验,提出了复合式路面层间抗剪强度评价方法,认为静压成型法结果与现场最为接近。袁明等[8]对复合式路面层间剪应力分析表明:适当增加沥青层厚度有利于降低层间剪应力。Wu等[9]研究发现,当层间接触条件改变时,层间最大剪应力变化幅度最大。孙培等[10]通过剪切试验研究了黏层油对层间抗剪强度的影响,认为高黏乳化沥青具有较好的抗剪能力。钟科等[11]发现聚氨酯黏结体系具有良好的拉拔强度和剪切强度,且拉拔强度和剪切强度随着固化时间的增加而增加。徐一超[12]发现不同黏结材料的层间剪切疲劳寿命随着应力比的增大而下降。王浩等[13]通过薄层橡胶沥青复合式路面层间抗剪特性试验,提出减小水泥路面刻槽间距可以有效提高复合界面抗剪强度。徐鸥明等[14]研究了水泥路面表面粗糙程度对铺装层路用性能的影响,认为混凝土板表面粗糙度对铺装层高温性能、层间抗剪强度及弯拉疲劳的衰减都有显著影响。Zhang[15]认为,层间剪切强度会随着试验温度的降低、交通荷载的增加以及正压力的增加而增加;此外,室内制备的试样比现场路面芯样的层间抗剪强度更大。
综上所述,针对复合式路面或水泥路面沥青薄层罩面,在剪切评价方法、罩面层影响、黏结层以及水泥路面表面粗糙等方面已有部分研究,但缺少各影响因素贡献的综合评价。基于此,本文选取了黏层油种类和用量、罩面层混合料类型和混凝土板表面特性等关键材料因素,通过直接剪切试验研究了复合结构层间剪切强度变化规律;基于灰色理论,分析了各因素影响程度,并推荐出较优的薄层沥青罩面结构层方案,以期能够为实际工程应用提供理论支持和技术指导。
1 原材料
1.1 水泥技术性质及混凝土级配
水泥采用普通硅酸盐水泥,强度等级为42.5,技术性质如表1所示。水泥混凝土配合比如表2所示。
表1 水泥主要性质
Table 1 Main properties of cement
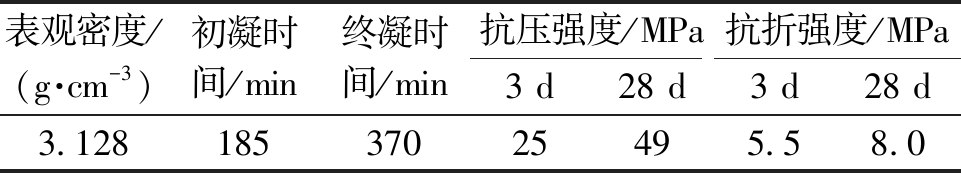
表观密度/(g·cm-3)初凝时间/min终凝时间/min抗压强度/MPa抗折强度/MPa3 d28 d3 d28 d3.12818537025495.58.0
表2 水泥混凝土配合比
Table 2 Mix proportion of cement concrete

类型用量/(kg·m-3)砂率/%水灰比水泥480300.45砂660300.45碎石1 200300.45
1.2 黏层油
本文选择了普通乳化沥青、SBS改性乳化沥青、自制高性能乳化沥青作为黏层油,研究它们对旧水泥路面加铺罩面层间抗剪强度的影响。3种不同种类乳化沥青技术指标如表3所示。
表3 3种乳化沥青主要性质
Table 3 Main properties of three types of emulsified asphalt
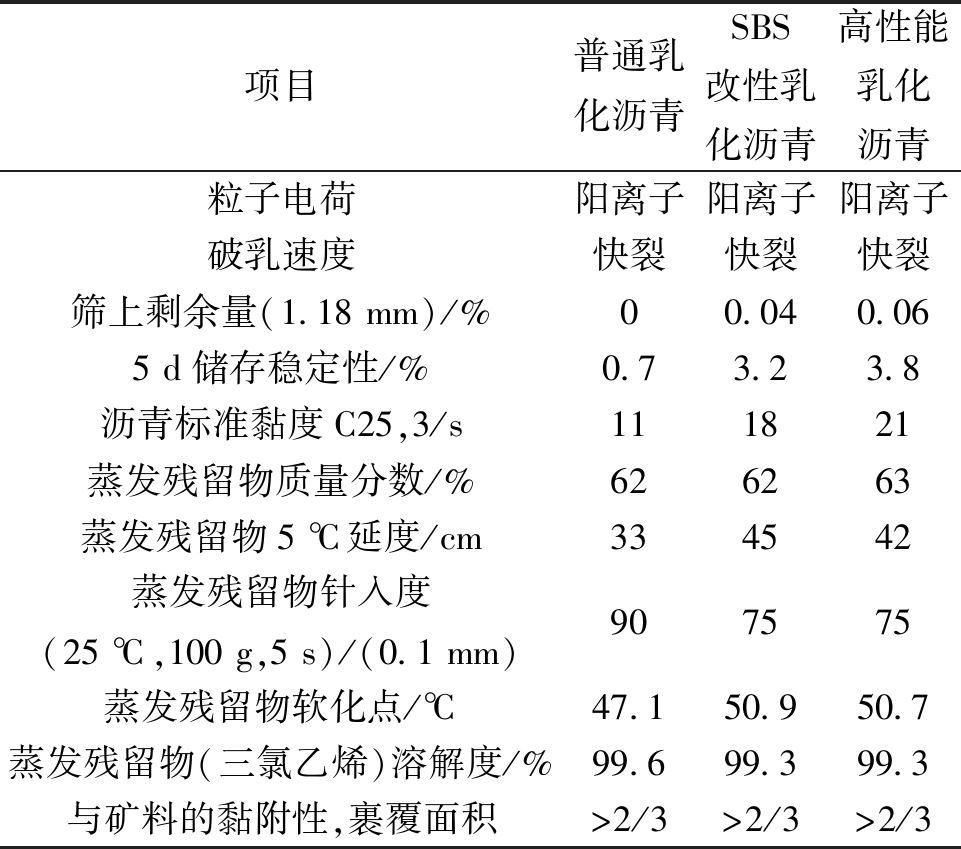
项目普通乳化沥青SBS改性乳化沥青高性能乳化沥青粒子电荷阳离子阳离子阳离子破乳速度快裂快裂快裂筛上剩余量(1.18 mm)/%00.040.065 d储存稳定性/%0.73.23.8沥青标准黏度C25,3/s111821蒸发残留物质量分数/%626263蒸发残留物5 ℃延度/cm334542蒸发残留物针入度(25 ℃,100 g,5 s)/(0.1 mm)907575蒸发残留物软化点/℃47.150.950.7蒸发残留物(三氯乙烯)溶解度/%99.699.399.3与矿料的黏附性,裹覆面积>2/3>2/3>2/3
1.3 沥青及罩面层混合料级配
罩面层混合料所用沥青为SBS改性沥青,其主要技术性质如表4所示。选择了3种不同类型的级配(AC-10、SMA-10和DTFC-10)作为罩面层混合料,所用集料为坚硬、清洁、干燥、无风化的片麻岩和石灰岩磨制矿粉,混合料级配如表5所示。
表4 SBS改性沥青主要技术性质
Table 4 Main technical properties of SBS modified asphalt

指标指标值针入度(25 ℃,100 g,5 s)/(0.1 mm)70针入度指数PI0.16延度(5 cm/min,5 ℃)/cm38软化点(环球法)/℃81135 ℃布氏旋转黏度/(Pa·s)2.1与集料的黏附性/级525 ℃弹性恢复/%85贮存稳定性(离析,48 h软化点差)/℃1.8
表5 罩面层沥青混合料级配
Table 5 Gradations of thin asphalt overlays mixtures %
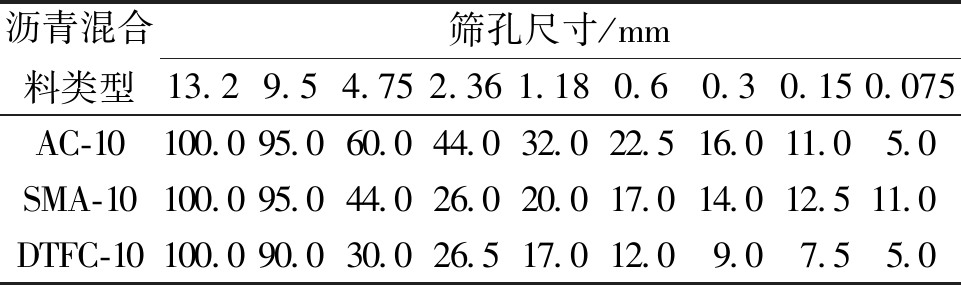
沥青混合料类型筛孔尺寸/mm13.29.54.752.361.180.60.30.150.075AC-10100.095.060.044.032.022.516.011.05.0SMA-10100.095.044.026.020.017.014.012.511.0DTFC-10100.090.030.026.517.012.09.07.55.0
2 抗剪强度实验方案
2.1 试样制备
为了模拟实际工程,本文采用“水泥混凝土板+黏层油+超薄沥青功能层”的复合结构。试样制备步骤如下。
(1)预制水泥混凝土板。参照《公路水泥混凝土路面施工技术细则》[6]在30 cm×30 cm×5 cm的车辙模具中成型C40水泥混凝土板。
(2)涂刷黏层油。去掉水泥混凝土板表面浮浆;按照试验设计,对混凝土板分别进行凿毛、刻槽和原状处理,并用毛刷将表面浮灰清扫干净;将水泥混凝土板装入试模内,涂刷黏层油。
(3)加铺薄层沥青罩面。涂刷黏层油后立即将拌好的罩面层混合料由四周向中间均匀摊铺在水泥混凝土板上,采用轮碾仪压实,控制罩面层厚度为2.5 cm。
(4)钻芯。待复合板完全冷却后,用钻芯机钻出直径为10 cm的芯样,以供试验用。
2.2 剪切试验
采用直剪仪对制成的复合试件进行层间直接抗剪试验,竖向荷载为0.2 MPa,剪切速率为20 mm/min,试验温度为25 ℃。
3 结果与分析
3.1 黏层油种类对层间抗剪强度的影响
罩面层通过黏层油与原有路面黏结成为整体,其稳定性取决于层间黏结强度,而层间黏结强度又受黏层油种类、用量、罩面层、原路面表面粗糙度等影响。通常,黏层材料的黏度越大,罩面层与原路面黏结越牢固,则罩面层抵抗剪切变形的能力就越强。反之,如果黏层材料的黏度较小,层间可能会成为薄弱环节,不足以承受罩面层传递下来的车轮水平荷载诱发的剪应力,从而使罩面层产生推移破坏。
不同黏层油黏附作用不一样,其用量与底层和铺装层材料有关,普通乳化沥青喷洒量约为0.5~0.7 L/m2,SBS改性乳化沥青约为0.6~1.2 L/m2。为了比较不同黏层黏附效果,参照经验,3种乳化沥青用量都为0.8 L/m2。3种乳化沥青黏层油复合试件的层间抗剪强度试验结果如图1所示。
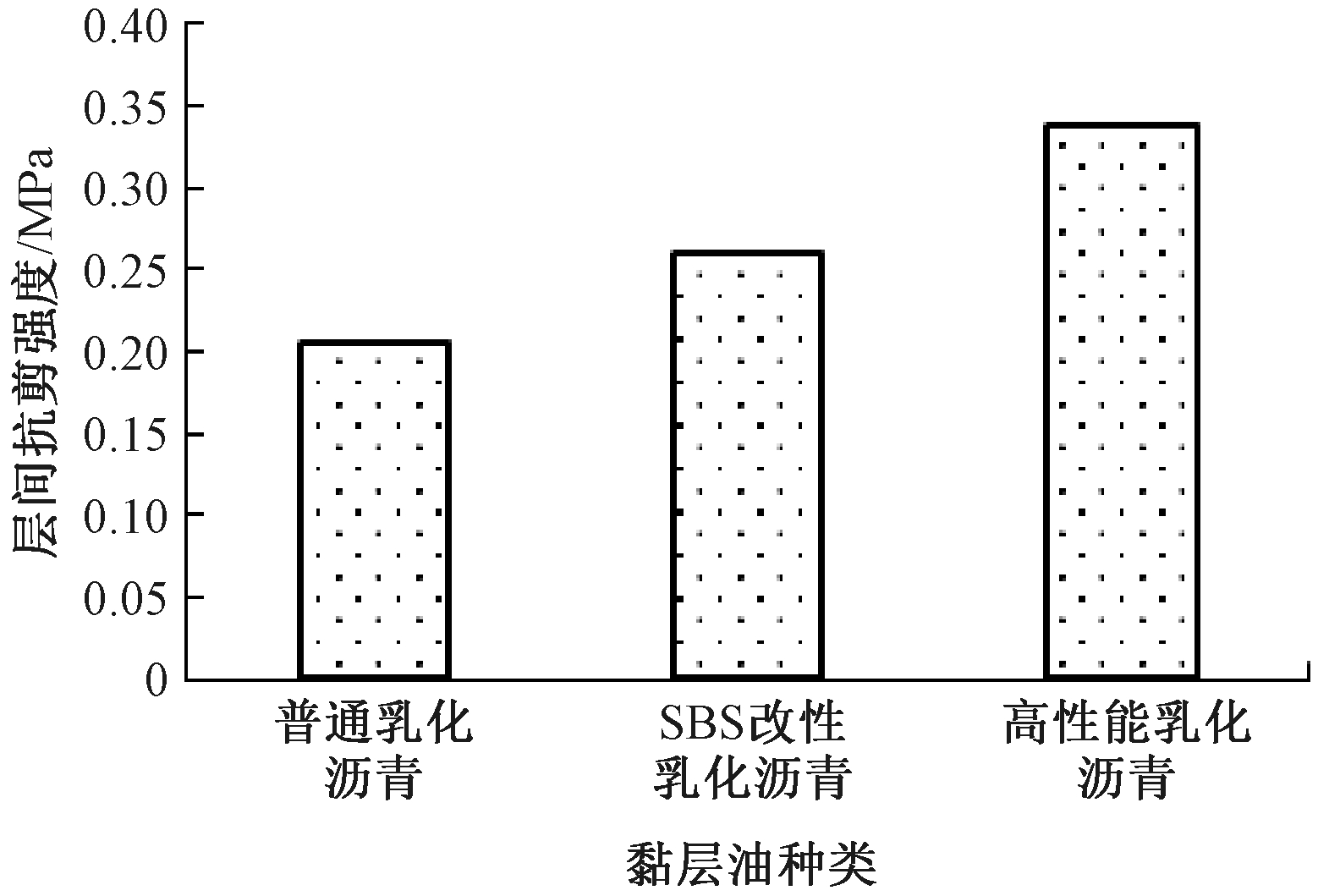
图1 黏层油种类对层间抗剪强度的影响
Figure 1 Effect of types of tack coat oil on interlayer shear strength
由图1可以看出,不同黏层油对层间抗剪强度的影响排序为:高性能乳化沥青>SBS改性乳化沥青>普通乳化沥青,其中普通乳化沥青和SBS改性乳化沥青的层间抗剪强度分别为高性能乳化沥青的61 %和77 %。由此可见,采用黏度较高的黏层油对改善层间抗剪强度有益。
3.2 黏层油用量对层间抗剪强度的影响
采用高性能乳化沥青,黏层油用量按照0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0、1.2 L/m2进行喷洒。不同黏层油用量的复合试件的层间抗剪强度试验结果如图2所示。
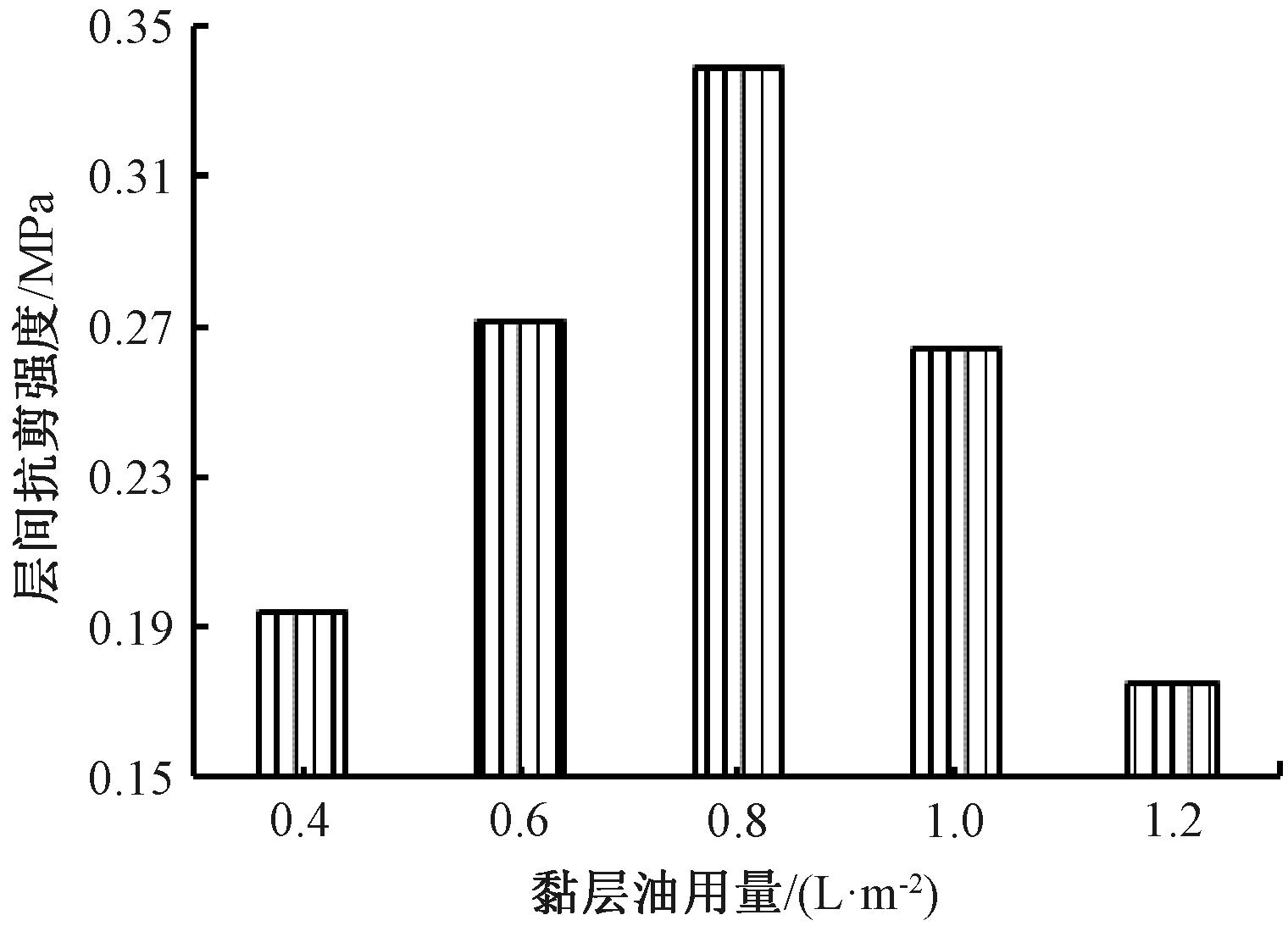
图2 黏层油用量对层间抗剪强度的影响
Figure 2 Effect of content of tack coat oil on interlayer shear strength
由图2可知,随着黏层油用量的增加,层间抗剪强度呈先增大后减小的趋势,且黏层油存在最佳用量。这是因为黏层油用量过少时,罩面层与原路面局部缺少黏结;而用量过多时,富余的黏层油成为自由沥青,在层间起润滑作用。当黏层油用量为0.8 L/m2时,黏层油恰好完全充填上下层之间,并形成了结构沥青,因此层间抗剪强度值达到最大。
3.3 罩面层混合料类型对层间抗剪强度的影响
3种罩面层混合料类型复合试件的层间抗剪强度试验结果如图3所示。
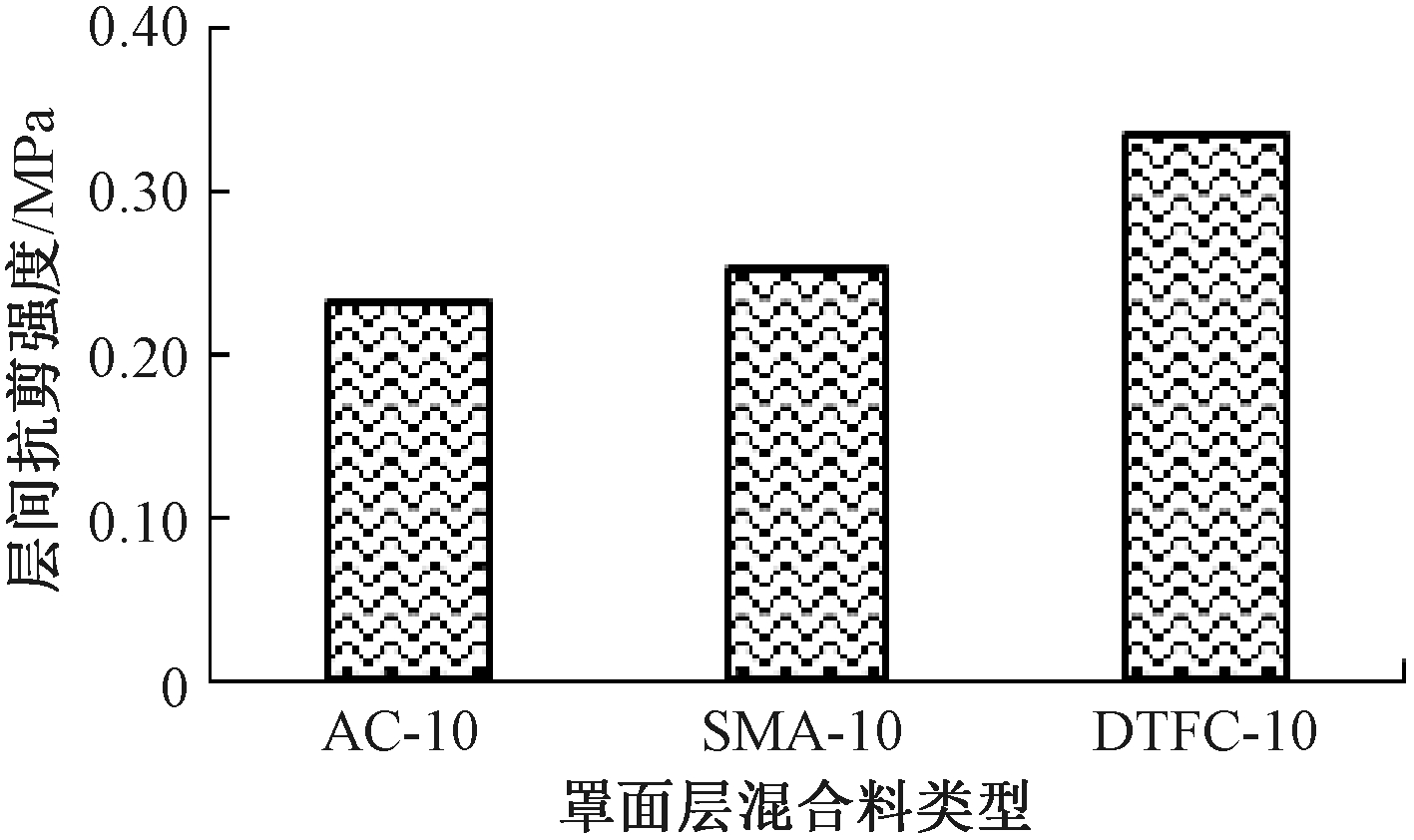
图3 混合料类型对层间抗剪强度的影响
Figure 3 Effect of types of mixture on interlayer shear strength
试验结果表明,罩面层混合料类型对层间抗剪强度的影响排序为:DTFC-10>SMA-10>AC-10。这是因为超薄磨耗层DTFC-10矿料级配属于一种骨架空隙结构,便于乳化沥青中水分排出,同时在碾压后在层间形成类似“铆钉”的结构,提高了层间摩阻力,因而层间抗剪强度最高,而都属于密实结构的SMA-10和AC-10的层间抗剪强度相差不大。
3.4 水泥路面板粗糙度对层间抗剪强度的影响
在实际工程中,在水泥混凝土路面加铺罩面前,通常会对混凝土板表面进行粗糙处理,以增强层间黏结力。本文模拟了原状、凿毛和刻槽等3种表面粗糙情况,利用手工铺砂法和摆式摩擦仪评价了不同表面纹理特性,结果如表6所示。
表6 不同处理方式的混凝土板表面特性
Table 6 Surface characteristics of concrete slabs with different treatment methods
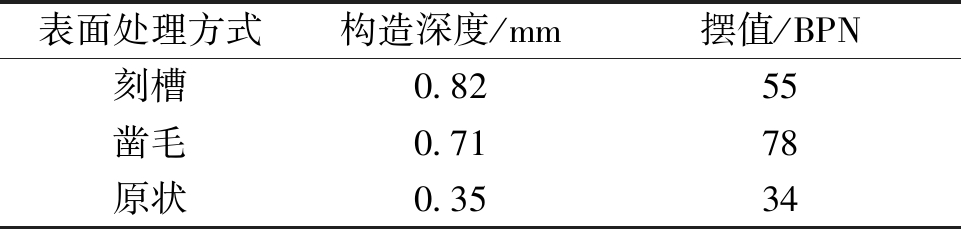
表面处理方式构造深度/mm摆值/BPN刻槽0.8255凿毛0.7178原状0.3534
3种表面处理方式复合试件层间抗剪强度试验结果如图4所示。
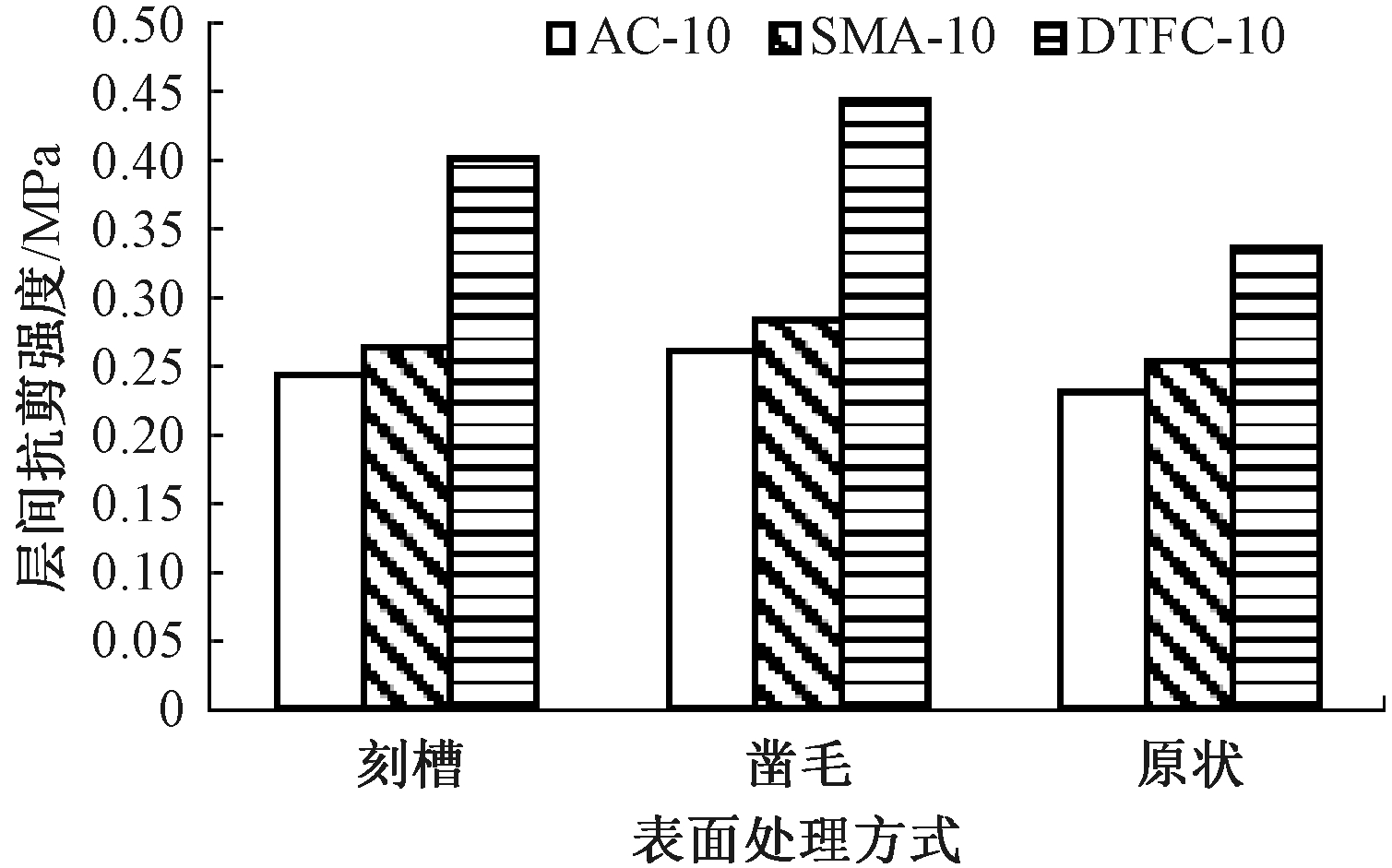
图4 混凝土板表面处理方式对层间抗剪强度的影响
Figure 4 Effect of surface treatment methods of concrete slab on interlayer shear strength
由图4可知,不同表面处理方式对层间抗剪强度的影响排序为:凿毛>刻槽>原状。这是因为凿毛形成的纹理方向具有随机性,构造比较丰富;而刻槽的纹理构造虽然较大,但具有方向性;原状表面主要是砂浆层的细观构造,宏观构造很小,对层间黏结和摩阻力均不及刻槽与凿毛。同时,罩面层采用DTFC-10时,在3种表面处理方式中其层间抗剪强度都明显高于其他2种混合料。由此可见,混凝土板表面粗糙程度对层间抗剪强度有积极影响。
3.5 各影响因素的关联度分析
本文通过灰色系统理论研究影响结构层层间抗剪强度各因素的关联程度。分析步骤如下。
(1)确定分析数列。以层间抗剪强度作为参考数列(R),以黏层油用量(C1)和标准黏度(C3)、罩面层混合料4.75 mm通过率(C2)和水泥板表面摆值(C4)作为比较数列,则原始数据如表7所示。
表7 层间抗剪强度原始数列
Table 7 Original sequence of interlayer shear strength
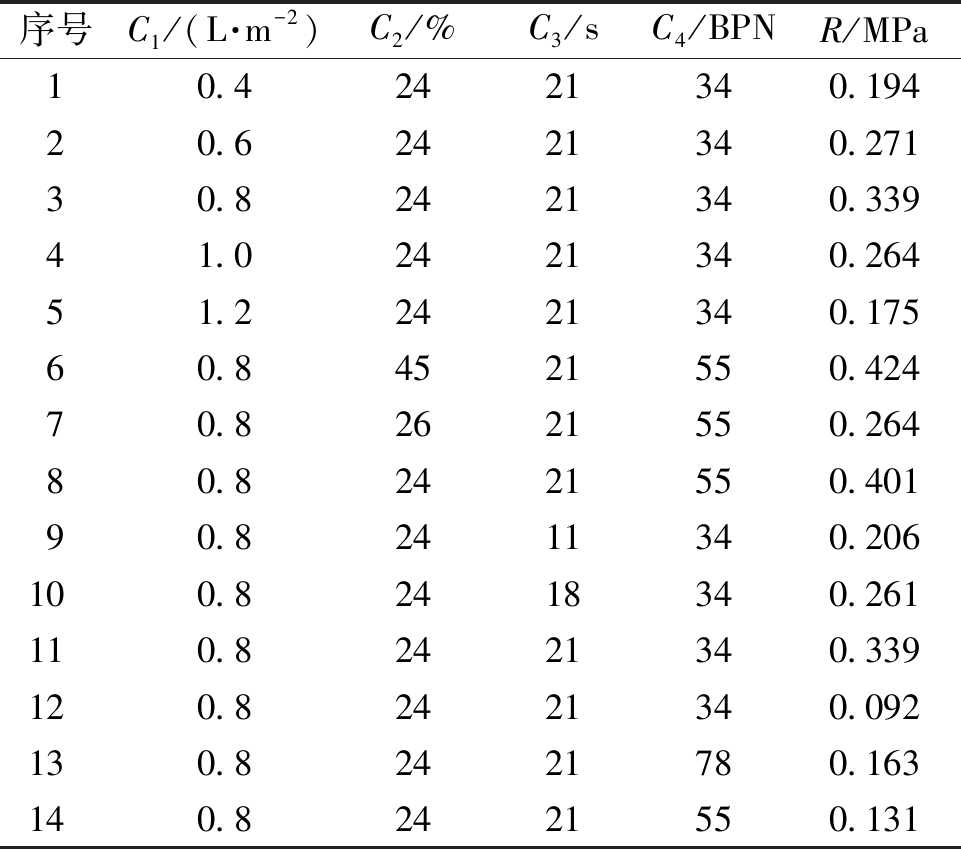
序号C1/(L·m-2)C2/%C3/sC4/BPNR/MPa10.42421340.19420.62421340.27130.82421340.33941.02421340.26451.22421340.17560.84521550.42470.82621550.26480.82421550.40190.82411340.206100.82418340.261110.82421340.339120.82421340.092130.82421780.163140.82421550.131
(2)对表7中的数列进行均值化处理,使试验数据无纲量化并计算求差序列。
(3)计算灰关联系数,其结果见表8。
表8 不同因素灰关联系数
Table 8 Grey correlation coefficient of different factors
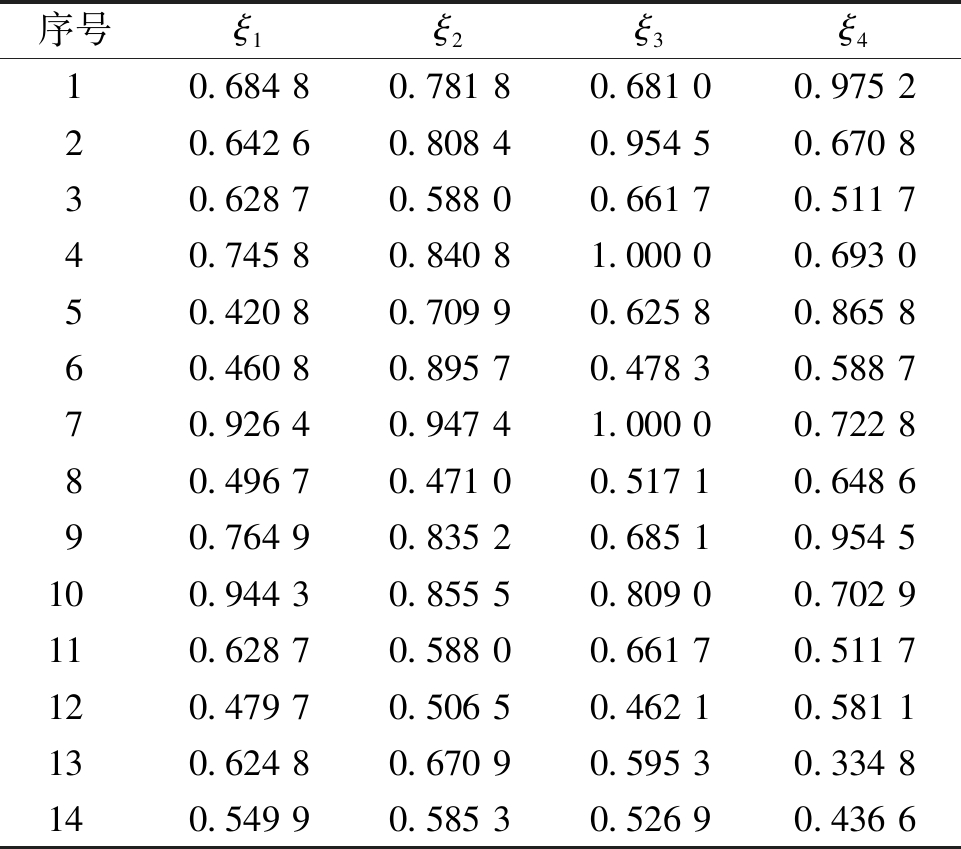
序号ξ1ξ2ξ3ξ410.684 80.781 80.681 00.975 220.642 60.808 40.954 50.670 830.628 70.588 00.661 70.511 740.745 80.840 81.000 00.693 050.420 80.709 90.625 80.865 860.460 80.895 70.478 30.588 770.926 40.947 41.000 00.722 880.496 70.471 00.517 10.648 690.764 90.835 20.685 10.954 5100.944 30.855 50.809 00.702 9110.628 70.588 00.661 70.511 7120.479 70.506 50.462 10.581 1130.624 80.670 90.595 30.334 8140.549 90.585 30.526 90.436 6
(4)计算灰关联度,其结果见表9。
表9 不同因素灰关联度
Table 9 Grey correlation degree of different factors
因素R1R2R3R4关联度0.6430.7200.6900.657
由表9可以看出,各种影响因素的排序结果为罩面层混合料类型>黏层油种类>水泥板表面粗糙程度>黏层油用量。由此可见,罩面层混合料类型对水泥路面加铺层间抗剪强度影响最为显著。因此,在改善水泥混凝土路面加铺罩面抗剪强度时,可从罩面层混合料类型选择入手,其次是黏层油类型,同时,水泥板表面粗糙程度和黏层油用量也应重视。
4 结论
(1)黏层油种类对层间抗剪强度有显著影响,采用高性能乳化沥青作为黏层油可提高层间黏结,从而增大层间抗剪强度;就提高层间抗剪强度而言,黏层油用量存在最佳值。
(2)罩面层混合料类型对层间抗剪强度有显著影响,采用骨架空隙型混合料易与下层形成嵌挤接触,对改善层间抗剪稳定性有利。
(3)水泥混凝土板表面粗粗程度对层间抗剪强度也有积极影响,均匀、粗糙的宏细观纹理构造有利于提高层间抗剪强度。
(4)灰关联分析表明,就层间抗剪强度而言,罩面层混合料类型最为重要,其次是黏层油,水泥混凝土板表面特性和黏层油用量也有一定影响。
(5)综合试验结果,推荐最优结构层组成方案为:超薄DTFC-10功能层+高性能乳化沥青黏层油+水泥混凝土板凿毛+黏层油洒布量为0.8 L/m2。
(6)由于水泥路面薄层沥青罩面结构在长期使用过程中受众多因素作用,长期层间抗剪特性需进一步评估。
[1] XU O M, HAN S, LIU Y M, et al. Experimental investigation surface abrasion resistance and surface frost resistance of concrete pavement incorporating fly ash and slag[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2021, 22(14): 1858-1866.
[2] KARPUZ O, UNIVERSITY G, Vefa AKPINAR M, et al. Effects of fine aggregate abrasion resistance and its fineness module on wear resistance of Portland cement concrete pavements[J]. Journal of Construction, 2017, 16(1): 126-132.
[3] REN W Y, HAN S, LI J, et al. Investigation of the relative abrasion resistance of concrete pavement with chip-sprinkled surfaces[J]. Wear, 2017, 382: 95-101.
[4] 苏卫国, 孙浩. 旧水泥混凝土路面直接加铺薄层沥青罩面方案选择分析[J]. 公路工程, 2015, 40(2): 169-173.
SU W G, SUN H. Scheme selection and analysis of asphalt ultra-thin overlayer laying on the old cement concrete pavement directly[J]. Highway Engineering, 2015, 40(2): 169-173.
[5] 楚留声, 王启源, 王帅起, 等. 反复荷载下CRC梁柱节点纵筋黏结性能试验研究[J]. 郑州大学学报(工学版), 2022, 43(4): 74-79.
CHU L S, WANG Q Y, WANG S Q, et al. Experimental study on the bonding performance of longitudinal reinforcement in CRC beam-column joints under cyclic loads[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University (Engineering Science), 2022, 43(4): 74-79.
[6] NIAN T F, GE J G, LI P, et al. Influence of multiple factors on the shear fatigue resistance of asphalt pavement interlayer adhesive materials[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2020, 32(9): 04020251.
[7] 曹明明, 黄晚清, 陆阳, 等. 复合式路面层间剪切性能试验和评价方法[J]. 公路交通科技, 2018, 35(4): 40-48.
CAO M M, HUANG W Q, LU Y, et al. Test and evaluation method of interlaminar shear property of composite pavement[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2018, 35(4): 40-48.
[8] 袁明, 凌天清, 张睿卓, 等. 复合式路面层间剪应力分析[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 30(6): 1318-1322, 1352.
YUAN M, LING T Q, ZHANG R Z, et al. Analysis on inter-laminar shear stress of composite pavement[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science), 2011, 30(6): 1318-1322, 1352.
[9] WU S H, CHEN H X, ZHANG J P, et al. Effects of interlayer bonding conditions between semi-rigid base layer and asphalt layer on mechanical responses of asphalt pavement structure[J]. International Journal of Pavement Research and Technology, 2017, 10(3): 274-281.
[10] 孙培, 韩森, 吕晓霞, 等. 用于粘结层的高性能乳化沥青制备与性能评价[J]. 材料导报, 2016, 30(14): 125-129, 144.
SUN P, HAN S, LU X X, et al. Development and performance evaluation of high-performance emulsified asphalt for tack coat[J]. Materials Review, 2016, 30(14): 125-129, 144.
[11] 钟科, 王雪, 张勐, 等. 单组份聚氨酯固化规律及黏结特性研究[J]. 郑州大学学报(工学版), 2021, 42(6): 80-84, 92.
ZHONG K, WANG X, ZHANG M, et al. Curing and adhesive characteristics of monocomponent polyurethane binders[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University (Engineering Science), 2021, 42(6): 80-84, 92.
[12] 徐一超. 加铺于旧沥青路面的薄层罩面层间剪切疲劳性能研究[J]. 北方交通, 2020(3): 57-59, 63.
XU Y C. Research on interlayer shear fatigue performance of thin-layer cover on old asphalt pavement[J]. Northern Communications, 2020(3): 57-59, 63.
[13] 王浩, 胡松山, 任少博. 薄层橡胶沥青复合式路面层间抗剪特性试验[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 38(4): 29-38.
WANG H, HU S S, REN S B. Shear resistance test of thin layer rubber asphalt pavement interlayer[J]. Journal of Chang′an University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 38(4): 29-38.
[14] 徐鸥明, 韩森, 于静涛. 层间界面对混凝土桥面铺装结构性能的影响[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 29(5): 17-20, 53.
XU O M, HAN S, YU J T. Effect of interlayer interface on structural performance of concrete bridge deck pavement[J]. Journal of Chang′an University (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 29(5): 17-20, 53.
[15] ZHANG W G. Effect of tack coat application on interlayer shear strength of asphalt pavement: a state-of-the-art review based on application in the United States[J]. International Journal of Pavement Research and Technology, 2017, 10(5): 434-445.